Microbial transformation of diosgenin by Cunninghamella blakesleana AS 3.970 and potential inhibitory effects on P-glycoprotein of its metabolites†
Abstract
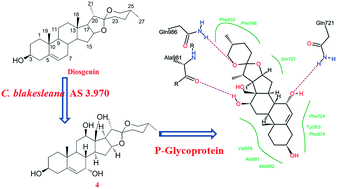
Microbial transformation of diosgenin ((25R)-spirost-5-en-3β-ol) using Cunninghamella blakesleana AS 3.970, afforded eleven polyhydroxylated derivatives, including seven previously unreported steroids, such as 25(R)-spirost-5-en-3β,7α,12β-triol (1), 25(R)-spirost-5-en-3β,7α,12β,15α,21-pentaol (3), 25(R)-spirost-5-en-3β,7α,12β,18-tetraol (4), 25(R)-spirost-5-en-3β,7α,12β,15α-tetraol (5), 25(R)-spirost-5-en-3β,7α,11α,21-tetraol (6), 25(R)-spirost-5-en-3β,7β,15α,21-tetraol (8), and 25(R)-spirost-5-en-3β,7β,12β,18-tetraol (10). The structures of metabolites 1–11 were elucidated by 1D-, 2D-NMR as well as HRESIMS techniques. Additionally, the biotransformation time-course of diosgenin by C. blakesleana AS 3.970 was presented. And the transformation pathway was also proposed on the basis of structural analyses and biotransformation time-courses. The P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitory effects of these metabolites 1–11 were evaluated in a adriamycin resistant human breast adenocarcinoma cell line (MCF-7/ADR) at 20 μM. And compounds 4 and 6 could increase the accumulation of adriamycin in MCF-7/ADR cells by approximately four times that of the control group, which suggested the significant potential P-glycoprotein inhibitory activities of 4 and 6. In silico docking analysis suggested that compound 4 had a similar P-gp recognition mechanism with verapamil (a classical inhibitor).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...