A novel triazine-aryl-bis-indole derivative inhibits both phosphodiesterase IV and expression of cell adhesion molecules†
Abstract
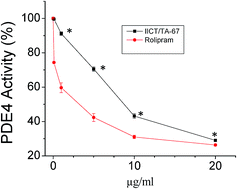
Asthma, like many inflammation related disorders, has a complex etiology. Drugs targeting multiple pathways may prove more efficacious in these complex disorders. Cyclic 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) phosphodiesterase IV (PDE IV) is one of the validated targets in bronchial asthma and despite availability of some therapeutic molecules targeting PDE IV, molecules with better properties are desired. Eosinophil/neutrophil infiltration into lung may also be an important component of bronchial asthma in which increased expression of epithelial cell adhesion molecules may play an important role. This study describes the synthesis of a novel class of compounds ‘triazine-aryl-bis-indoles’ having a catechol derived structure constituting a part of ‘triazine’ and a part of ‘bis-indole’ moiety on it. This class of molecules potently inhibited both phosphodiesterase IV and expression of cell adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. The best molecule of this class (compound 11) inhibited PDE IV activity in vitro, with an IC50 value of 14 μM compared to 12.7 μM for an existing drug rolipram. The compound 11 not only stabilized the cAMP level in human lung epithelial cells (L132) following stimulation with forskolin, but also inhibited TNF-α induced expression of cell adhesion molecules such as ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in human umbilical vein epithelial cells (HUVECs). It also significantly inhibited the adhesion of human neutrophils to the endothelial monolayer (IC50 = 17.86 μM) in a dose dependent manner. Its absolute bioavailability (in mice) was found to be 70% and its toxicity and pharmacokinetic profiles are excellent. The dual activity of this class of molecules suggests that this class of molecules could have broad therapeutic applications in neutrophil dominant diseases such as severe asthma, COPD and acute lung injury.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...