Concave gold nanoparticle-based highly sensitive electrochemical IgG immunobiosensor for the detection of antibody–antigen interactions
Abstract
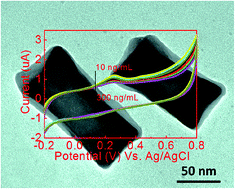
In this work, we report a novel electrochemical sensor for the label-free, real time and highly sensitive detection of antibody–antigen interactions based on concave gold nanocuboids (CAuNCs). In contrast to low-index facet gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) such as gold nanorods (AuNRs), the CAuNCs provide higher surface atoms with enhanced chemical activities, which can efficiently catalyse the oxidation reaction of amino groups on antibodies (anti-bovine IgG produced in rabbit). This leads to an obvious redox current response being observed in cyclic voltammetry (CV) measurements. Upon the introduction of an IgG antigen, a notable decrease of the anodic peak current was observed, which is attributed to the formation of an antigen–antibody complex between the IgG antigen and the antibody on the CAuNCs. The unique electrocatalytic property of the CAuNCs allows easy detection of the rabbit IgG antigen in a wide range of concentrations (from 10 to 200 ng mL−1), with a limit of detection (LOD) to 5 ng mL−1 (signal to noise ratio 3 (S/N = 3)) by using a CV method.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...