Influence of calcination temperature on the catalytic performance of Co3O4/GO nanocomposites for Orange II degradation†
Abstract
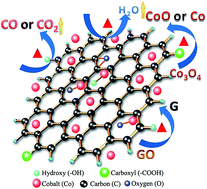
In this study, graphene oxide-supported cobalt oxide catalysts (Co3O4/GO), which are used to degrade Orange II from water via advanced oxidation processes based on sulfate radicals, are synthesized in situ as heterogeneous catalysts via a solvothermal method. The catalysts were calcined at different temperatures of 300 °C, 500 °C, 700 °C, and 900 °C for 2 h in N2 atmosphere. The catalytic activities of both uncalcined and calcined catalysts were studied at the same time. The results show that all the formed catalysts exhibit high catalytic activity, and the catalysts calcined at 900 °C have the best activity for the degradation of Orange II. X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) are employed to study the mechanism behind the change in catalytic activity. The analysis indicates that the change in the quantity of hydroxylated cobalt (Co–OH), the valence state of cobalt oxide and the reduction degree of graphene oxide (GO), which are all caused by calcination, are responsible for the change in catalytic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...