Photo and electronic excitation for low temperature catalysis over metal nanoparticles using an organic semiconductor†
Abstract
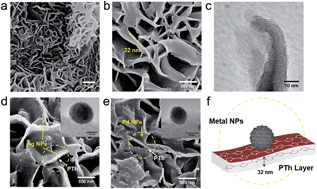
Simple supported metal catalysts are active for the destruction of a wide range of hazardous chemicals of environmental concerns, including CO, N2O and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), in air at elevated temperatures. However, they are severely restricted because of unfavourable enthalpy and intrinsic low activity under ambient conditions, in particular the inapplicability of using high temperatures in confined spaces. Here, we report a simple but significant means of electron promotion to metal nanoparticles by the use of an organic polythiophene as a support or support supplement, which gives rise to an active modified metal surface for selective catalysis at low temperatures with light or electromotive excitation. It is observed that the finite size of electronic structure of dispersed metal nanoparticles can be influenced by the conjugative bands of a polymer, which leads to the modification of its adsorptive properties. This renders the composite material active for a number of oxidation and decomposition reactions under ambient conditions, which outperforms the conventional catalysts. As a result, the present study forms a basis for further developments in the design and engineering of a new class of greener plastic nanocatalysts with facilitated electron promotion to metal catalysts for environmentally relevant chemical transformations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...