Biocompatible folate-modified Gd3+/Yb3+-doped ZnO nanoparticles for dualmodal MRI/CT imaging†
Abstract
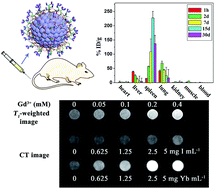
The development of multimodal imaging probes is highly desirable for clinical diagnosis and therapy because they combine the advantages of different imaging functionalities within a single nanoplatform and can provide complementary information from each imaging modality. Herein, we demonstrated our effects on the fabrication of a ZnO:Gd,Yb probe for MRI/CT imaging on the basis of the paramagnetic property of Gd3+ and the high X-ray absorption property of Yb3+. To increase the stability and biocompatibility, these nanoprobes were functionalized with folate (FA). The cytotoxicity and histological analysis show these nanoparticles (NPs) present low cytotoxicity even at a Gd3+ concentration as high as 30 μg mL−1 and have no obvious injury or inflammation in the susceptible organs (heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney). Upon intravenous injection, the uptake and deposition of FA-modified nanoprobes takes place primarily in the spleen, lung and liver, and but these NPs can be completely excreted out from the body of mice as time is prolonged. These nanoprobes not only exhibit a relatively higher longitudinal relaxivity (r1) of 6.29 mM−1 s−1 over the commercial Gd(III)-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid complexes, but also keep a strong X-ray attenuation property. In T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and X-ray computed tomography (CT) studies, they can efficiently induce positive contrast enhancement, demonstrating the potential of the as-prepared ZnO:Gd,Yb-FA NPs for the development of dualmodal MRI/CT molecular imaging probes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...