Biodiesel derived waste glycerol as an economic substrate for biosurfactant production using indigenous Pseudomonas aeruginosa†
Abstract
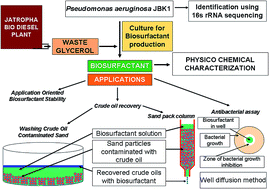
The present investigation demonstrates the utilization of biodiesel-derived crude glycerol as a low-cost substrate for the production of biosurfactant. Pseudomonas aeruginosa JBK1 was identified using 16s rRNA sequencing. A maximum of 3.9 g biosurfactant was obtained at 3% raw bio-glycerol having the critical micelle concentration (CMC) at nearly 540 mg l−1. The bacterium lowered the surface tension (ST) of culture medium up to 33.7 mN m−1 within 60 h of fermentation and showed better adhesion to the hydrophobic substrate surfaces. The biosurfactant formed stable emulsion with various hydrocarbons and achieved a maximum emulsion index of 62% with kerosene and xylene. The cell free culture supernatant exhibited a stable surface as well as emulsifying activity, and remained unaffected by the exposure of high temperature, pH and salinity. Mass spectrometric studies indicated that the purified product is glycolipid in nature. Sand pack column experiments showed a 10.8% recovery of crude oil from the column after treatment with the cell free culture supernatant. A maximum of 54.6% residual crude oil was removed through washing by the biosurfactant solution. The biosurfactant also exhibited potential antimicrobial activity against a variety of bacterial and fungal strains. The results suggest that the biosurfactant produced by the bacterium on waste glycerol may have potential application in hydrocarbon bioremediation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...