Amidoxime-functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica for selective sorption of U(vi)†
Abstract
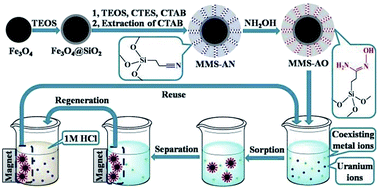
Amidoxime-functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica (MMS-AO) microspheres were synthesized through co-condensation of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and 2-cyanoethyltriethoxysilane (CTES) on the surface of silica-coated Fe3O4 followed by chemical modification of nitrile into amidoxime. The synthesized microspheres exhibit a typical sandwich structure with an inner core of Fe3O4, a middle layer of nonporous silica and an outer layer of amidoxime-functionalized mesoporous silica. Owing to the mesoporous structure and amidoxime functionalization, sorption of U(VI) by MMS-AO reaches equilibrium in 2 h of contact time with a maximum sorption capacity of 1.165 mmol g−1 (277.3 mg g−1) at pH = 5.0 ± 0.1 and T = 298 K, which is much higher than the results previously reported for other magnetic materials. The sorption process is strongly dependent on pH but independent of ionic strength, indicating that the predominant sorption mechanism is inner-sphere surface complexation. The selectivity of MMS-AO for U(VI) is remarkably improved in comparison with that of magnetic mesoporous silica without amidoxime functionalization. U(VI)-loaded MMS-AO can be conveniently separated from aqueous solutions with an external magnetic field and efficiently regenerated using 1 mol L−1 HCl with only a small decrease in U(VI) sorption capacity. These results suggest that MMS-AO shows promise as a future candidate for selective separation of U(VI) from aqueous solutions in possible real applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...