Facile one-pot fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs)-supported organocatalysts using phosphonate as an anchor point through direct co-precipitation method†
Abstract
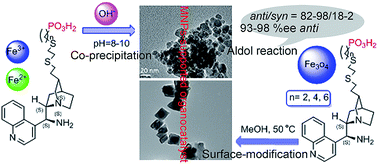
In this paper, a novel type of efficient, magnetically recoverable magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs)-supported 9-amino-9-deoxy-epicinchonidine organocatalysts were prepared through a facile co-precipitation method using phosphonic acid (–PO3H2) as an anchor point. These MNPs-supported organocatalysts possessed the high and tunable loading capacities of an organocatalyst (0.18–0.52 mmol g−1), 2–25 nm regular mesopores and 10.6–44.06 emu g−1 saturated magnetization. In the catalytic asymmetric aldol reactions of cyclohexanone with various o, m and p-substituted benzaldehydes in water, the aromatic aldehydes with electron-withdrawing substituents including-NO2, X and –CN afforded the relevant aldol adducts in excellent yields (86–100%) and steroselectivities (anti/syn = 82–98/18–2 and 93–98%ee anti). Moderate to good yields (36–97%) and steroselectivities (anti/syn = 82–96/18–4 and 75–97%ee anti) for the aromatic aldehydes with strong electron-donating substituents (–CH3 and –OCH3) were also satisfactorily achieved. Futhermore, these MNPs-supported organocatalysts could be quantitatively recovered from the reaction mixture using an external magnet, and reused six times with excellent catalytic performance (93%, anti/syn = 89/11 and 96%ee anti). Meanwhile, MNPs-supported organocatalysts, prepared by the surface-modification method, were investigated in detail as comparative samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...