Intermolecular interactions of CTAB and potential oxidation inhibitors: physico-chemical controlled approach for food/pharmaceutical function†
Abstract
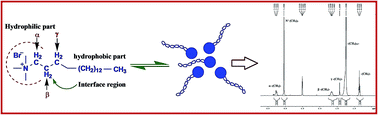
We report the impact of lipophilic oxidation inhibitors i.e. butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) on cationic surfactant, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) properties in short chain alcohols and their hydroalcoholic solutions. Considering the extensive employment of BHA and BHT in human products, controlled physicochemical approaches were taken into consideration. Principally, density (ρ), ultrasonic sound velocity (u) and viscosity (η) measurements were carried out at specific temperatures T = (298.15, 303.15 and 308.15) K. The physico-chemical parameters apparent molar volume (Vϕ) and apparent molar adiabatic compression (Kϕ,S) were calculated and revealed the existence of hydrophobic interactions whereas, viscosity measurements depicted the region of micellization. Additionally, 1H NMR spectroscopic study was employed to interpret the intermolecular interaction of antioxidants within the micellar structure. 1H NMR analysis suggested the intermolecular interaction especially in the hydrophilic head and interface region of the surfactant with regard to shifting obtained within spectrum.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...