Label-free cell phenotypic profiling identifies pharmacologically active compounds in two traditional Chinese medicinal plants†
Abstract
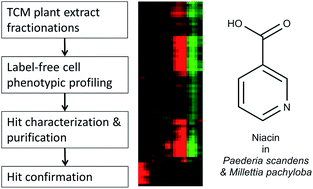
Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs) are widely used in clinical practice and natural products have been a rich resource for drug discovery. Identification of pharmacologically active chemical constituents is essential to the future of TCMs and natural product-based drug discovery. Here we report a label-free cell phenotypic profiling strategy to identify active fractions and compounds of two TCM plants including Paederia scandens (Lour.) Merri. (Jishiteng in Chinese) and Millettia pachyloba Drake (Duyuteng in Chinese), and to determine their mechanisms of action. The extracts of both plants were first fractionated to 160 fractions. Label-free cell phenotypic profiling afforded by a resonant waveguide grating biosensor in a microplate were then used to identify the active fractions acting at three different cell lines including A431, A549 and HT29. Mass spectroscopy-directed purification was then used to identify and purify active compounds. NMR and mass spectroscopy were used to determine the chemical structures of the active compounds, and pharmacological assays were used to elucidate their mechanisms of action. Using this strategy, we have discovered that both medicinal plants contain moderately high amount of niacin, an agonist for hydroxyl carboxylic acid receptor-2. Literature mining further suggests that the presence of niacin in Paederia scandens may be responsible for its antidyslipidemic effect found in clinic studies. This study demonstrates the potential of label-free cell phenotypic profiling for identifying active fractions and compounds of TCMs as well as elucidating their mechanisms of action.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...