Online monodisperse droplets based liquid–liquid extraction on a continuously flowing system by using microfluidic devices†
Abstract
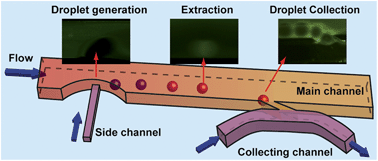
In this work, we developed a chip-based continuously flowing system for online liquid–liquid extraction by using monodisperse droplets, and the droplets containing target compounds after extraction were collected on the microchip. Monodisperse droplets of extracting reagent were on-chip generated and dispersed in continuously flowing sample solution, and then liquid–liquid extraction happened when organic droplets moved forward with sample solution flow. After liquid–liquid extraction, guiding tracks were designed in our system to capture the organic droplets, which allowed the aqueous solution flowing over at the same time. Structures of the microchip were optimized to achieve generation and collection of monodisperse droplets more efficiently. To verify the feasibility of droplet based liquid–liquid extraction on the established platform, we used aqueous solution containing 10 μM fluorescein sodium as sample solution and butanol as the extracting reagent to perform the whole procedures. Fluorescein sodium was successfully extracted by the butanol droplets, and the butanol droplets were successfully collected. The results demonstrated that the developed microfluidic device was a useful tool for monodisperse droplet based liquid–liquid extraction. As all the procedures including droplet generation, extraction and collection were performed on one chip, the established platform had the potential of time-resolved monitoring.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...