Easy amino-group modification of graphene using intermolecular forces for DNA biosensing
Abstract
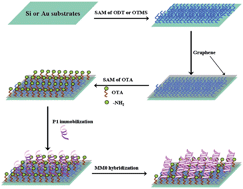
We demonstrated an easy and efficient approach to produce amino-group-functionalized graphene (G-NH2) for highly sensitive DNA biosensing through intermolecular interaction. The nucleotide molecules prefer to anchor onto the as-prepared G-NH2 surface rather than be immobilized on pristine graphene. The electrostatic interaction between the positive charges of the ionized amino on G-NH2 and the negative charges of phosphate groups on nucleotide chains enabled label-free probe DNA to be immobilized on the G-NH2 surface. The electrochemical performance and quality variations during the preparation of G-NH2 and nucleotide immobilization processes were determined by electrochemical measurements and quartz crystal microbalance in situ, respectively. Results showed that complementary target DNA could be hybridized with probe DNA within the concentration range of 0.1 nM to 200 nM, and the detection limit was 0.8 nM. Therefore, this kind of G-NH2 could be an alternative for DNA biosensing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...