Computational modelling and characterisation of nanoparticle-based tuneable photonic crystal sensors†
Abstract
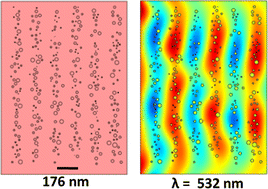
Photonic crystals are materials that are used to control or manipulate the propagation of light through a medium for a desired application. Common fabrication methods to prepare photonic crystals are both costly and intricate. However, through a cost-effective laser-induced photochemical patterning, one-dimensional responsive and tuneable photonic crystals can easily be fabricated. These structures act as optical transducers and respond to external stimuli. These photonic crystals are generally made of a responsive hydrogel that can host metallic nanoparticles in the form of arrays. The hydrogel-based photonic crystal has the capability to alter its periodicity in situ but also recover its initial geometrical dimensions, thereby rendering it fully reversible and reusable. Such responsive photonic crystals have applications in various responsive and tuneable optical devices. In this study, we fabricated a pH-sensitive photonic crystal sensor through photochemical patterning and demonstrated computational simulations of the sensor through a finite element modelling technique in order to analyse its optical properties on varying the pattern and characteristics of the nanoparticle arrays within the responsive hydrogel matrix. Both simulations and experimental results show the wavelength tuneability of the sensor with good agreement. Various factors, including nanoparticle size and distribution within the hydrogel-based responsive matrices that directly affect the performance of the sensors, are also studied computationally.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...