Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanosensor for mercury ion detection based on functionalized silver nanoparticles†
Abstract
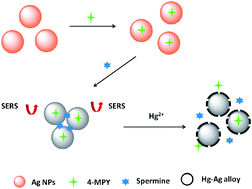
In this work, a simple, rapid and ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) nanosensor was developed for mercury ion (Hg2+) detection based on 4-mercaptopyridine (4-MPY) functionalized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) (4-MPY-AgNPs) in the presence of spermine. Here, the spermine would bind AgNPs through Ag–N bonds and induce remarkable aggregation of AgNPs, and thereby would generate significantly enhanced Raman intensity of the reporter molecule 4-MPY. Followed by the addition of Hg2+, the formation of the Hg–Ag alloy blocked the adsorption of 4-MPY and spermine, resulting in the dispersion of 4-MPY-AgNPs and thus decreasing the Raman intensity, by which the Hg2+ could be sensed by SERS. A good linearity was obtained in the range of 1–100 nM (R2 = 0.987), and the relative standard deviation was between 0.85 and 5.50%. The spermine-induced accumulation of 4-MPY-AgNPs largely enhanced the SERS responses, leading to a high detectability up to 0.34 nM. A real water sample with spiked Hg2+ was also analyzed, presenting satisfactory recoveries ranging from 94.5 to 108.5%, confirming the practicability of the SERS nanosensor based method.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...