Quantum chemical calculation studies for interactions of antiwear lubricant additives with metal surfaces†
Abstract
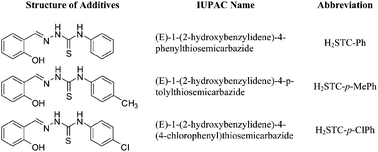
Theoretical calculations based on density functional theory (DFT) have been performed to correlate experimentally observed antiwear properties of Schiff base lubricant additives derived from condensation of salicylaldehyde with N-phenylthiosemicarbazide, [(E)-1-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-phenylthiosemicarbazide; H2STC-Ph], N-p-tolylthiosemicarbazide [(E)-1-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-p-tolylthiosemicarbazide; H2STC-p-MePh] and N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiosemicarbazide, [(E)-1-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)thiosemicarbazide; H2STC-p-ClPh] with their chemical structure. antiwear properties have been discussed on the basis of the interactions between the additive molecules and the metal surface. In order to compare the antiwear behavior of different additives, various parameters such as frontier molecular orbital energy EHOMO (Energy of Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital), ELUMO (Energy of Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital), the energy gap (ΔE), mutual orbitals’ interactions between additive molecules and metal surface (ΔE1 & ΔE2), global properties (hardness and softness) and the dipole moment have been calculated and correlated with the respective energies of the metal surface. The quantum chemical calculations (QCC) have shown that the wear-reducing behavior of Schiff bases increases with an increase in EHOMO, decrease in ELUMO, decrease in the energy gap between ELUMO and EHOMO and increase in the dipole moment of the additives. The results obtained by quantum chemical calculations are in good agreement with the experimental results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...