Lipophilic phenolic compounds (Lipo-PCs): emerging antioxidants applied in lipid systems
Abstract
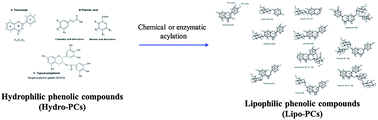
Oxidative degradation of lipids is one of the most important factors for quality preservation in the food or cosmetics industry. Addition of antioxidants could prevent or delay lipid oxidation. However, the applications of synthetic antioxidants have been restricted for their potential carcinogenic effects and toxicity. Lipophilic phenolic compounds (Lipo-PCs) are emerging lipid antioxidants, which could be found in nature with minor content. Synthesis of Lipo-PCs from natural hydrophilic phenolic compounds (Hydro-PCs) is on-going by chemical or enzymatic acylation. Chemical synthesis is a traditional method while enzymatic synthesis is a safer and more environmentally friendly process. In this review, key parameters to influence the acylation synthesis of Lipo-PCs and crucial factors for the extrinsic efficiency of given antioxidant reactivity were introduced as a highly promising prospect. The key parameters during enzymatic acylation include enzymes, phenolic substrates, solvents and acyl donors. Antioxidant efficiency of Lipo-PCs in lipid systems depends on various factors and hydrophobicity is the one which cannot be ignored. Polar paradox and cut-off hypothesis are two theories to illustrate different antioxidant behaviour of hydrophobic antioxidants in lipids systems, which give us a guideline to synthesize highly efficient antioxidants with appropriate hydrophobicity and understand their antioxidant mechanisms in different mediums.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...