Rapid synthesis of gold nanostructures with cyclic and linear ketones†
Abstract
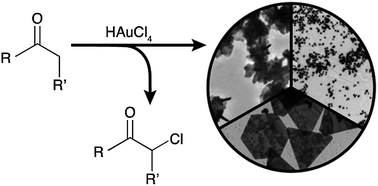
Colloidal gold nanoparticles were synthesised in aqueous solution by reaction of chloroauric acid with a range of simple aliphatic cyclic (cyclopentanone, cyclohexanone, cycloheptanone and cyclohexanedione) and linear (acetone and 3-hexanone) ketone reagents, at room temperature. The rate of reaction and particle morphology was found to be controlled by the enol content and solubility of the ketone. Cyclohexanediones produced a variety of small 20 nm particles in under 5 minutes, or larger gold nanostars, depending on the ketone isomer. Cyclopentanone was shown to produce near monodisperse 20 nm particles after 13 hours, and cycloheptanone gave polydisperse particles, but in only 50 minutes. However the linear ketones, 3-hexanone and acetone, did not produce stable colloidal suspensions. The mechanism of gold nanoparticle formation via reaction of ketones with chloroauric acid is discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...