Chemoselective reduction of graphene oxide and its application in nonvolatile organic transistor memory devices†
Abstract
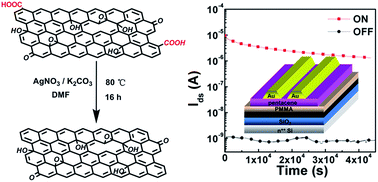
A facile method for the chemoselective reduction of graphene oxide (CrGO) has been developed via silver(I)-catalyzed decarboxylation. CrGO was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. CrGO can be well-dispersed in most polar solvents, facilitating its nanosheet thin film preparation via a spin coating solution process for device fabrication. A proof of concept nonvolatile organic transistor memory device using CrGO as the charge-trapping layer showed a larger memory window of over 60 V and a higher ON/OFF current ratio of up to 104 compared to that of the precursor, graphene oxide (GO).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...