Cellulose nanocrystals as a novel support for CuO nanoparticles catalysts: facile synthesis and their application to 4-nitrophenol reduction†
Abstract
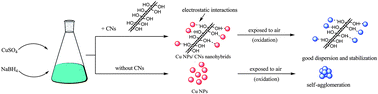
Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs) have attracted considerable attention due to their excellent catalytic activities in various organic transformation reactions. However, their widespread application is limited because of their self-agglomeration in solution and the resulting reduced catalytic performance. Here we report that cellulose nanocrystals (CNs), which are sustainable and globally available in large quantities from plants, can be used as a novel support for copper oxide (CuO) NPs with enhanced catalytic performance. The high surface area of CNs and the abundant hydroxyl groups-induced immobilization of CuO NPs make the CNs-supported CuO NPs nanohybrids significantly stable, with CuO NPs/CNs suspensions remaining well-distributed even after a month. The obtained nanohybrids exhibited much higher catalytic activities than the unsupported and other materials-supported metal NPs (e.g. graphene oxide-supported CuO) in the catalyzed reduction of 4-nitrophenol. The facile processes used to make the nanohybrids catalysts are readily scalable to industrial levels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...