Biocompatible acid-labile polymersomes from PEO-b-PVA derived amphiphilic block copolymers†
Abstract
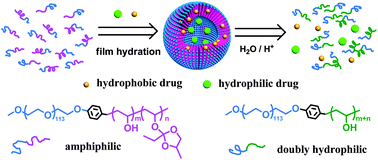
A family of amphiphilic block copolymers with pendent ortho ester groups were synthesized by modifying the double hydrophilic block copolymer PEO114-b-PVA240 with 2-ethylidene-4-methyl-1,3-dioxolane (EMD) under mild conditions (30 °C). The degree of modification (DM) of the ortho ester groups can be tuned by simply varying the feed ratio of EMD to the hydroxyl groups in the PVA block. These block copolymers are stable in an anhydrous environment. Laser light scattering (LLS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) measurements revealed that in weakly basic aqueous buffer, these amphiphilic block copolymers self-assembled into aggregates with different size and morphology, ranging from solid-like spherical nanoparticles to polymersomes as the DM increased. The acid-triggered dissociation behaviour of the aggregates were studied by LLS, nile red (NR) fluorescence and TEM. The copolymer aggregates dissociated faster in a buffer with the lower pH; the dissociation rate of the aggregates became faster for the copolymers with lower DM. The polymersomes can load both hydrophilic biomacromolecules like lysozyme and hydrophobic anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX). The drug-loaded polymersomes were stable in neutral phosphate buffer for at least 6 h with a payload leakage of less than 25% in 12 h at 37 °C; however, significant acid-triggered payload release was accomplished even at a mildly acidic pH (6.0). Finally, the DOX-loaded polymersomes exhibited a concentration-dependent toxicity to MCF-7 and HeLa cells while the copolymers themselves are non-toxic.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...