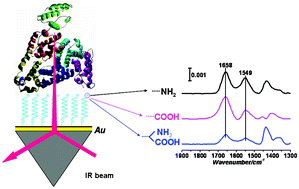
Zwitterionic materials have recently attracted extensive attention as antifouling materials due to their stability regardless of the temperature. Here we study the adsorption of one plasma protein, human serum albumin (HSA), on the zwitterionic D-penicillamine-modified gold surface by surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA) spectroscopy. In comparison with the adsorption of HSA on a cysteamine (positive charge) and mercaptopropionic acid (negative charge)-modified gold surface, the amount of adsorbed HSA on the zwitterionic surface was less, but the native structure of the adsorbed HSA was retained, which revealed that the zwitterionic surface was resistant to the protein adsorption. The kinetics study showed that the adsorption of HSA on the three surfaces happened in one of two ways: reversible adsorption or irreversible adsorption resulting from protein unfolding. However, the time constants involved were dramatically larger when HSA was adsorbed on the zwitterionic surface, which further proved its antifouling property. The mechanism was revealed by monitoring the water adsorption. It was found that strongly hydrogen-bonded water played an important role in the protein resistance of the zwitterionic D-penicillamine-modified gold surface. In addition, competitive binding experiments with site markers revealed that HSA was adsorbed on the zwitterionic surface through domain IIA and IIIA and on the carboxylic acid-terminated surfaces through domain IIA.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...