Synergistic action of flavin containing NADH dependant azoreductase and cytochrome P450 monooxygenase in azoaromatic mineralization†
Abstract
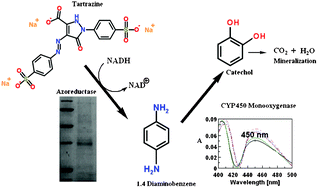
An alkaliphilic strain Bacillus lentus BI377 was isolated from contaminated soil of the textile area of Solapur, India. The strain was able to degrade almost 98% of recalcitrant azoic compounds by a mutually regulated process of azoreductase and a monooxygenase system. An enzyme activity study and a periodical carbon monoxide (CO) binding spectra study on a UV-visible spectrophotometer revealed that the intermediate amines formed by typical azoreduction (N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N cleavage), subsequently underwent hydroxylation by the cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (CYP450) system. Azoreductase was purified by chromatographic techniques and characterization by MALDI-TOF substantiated its identity as FMN containing NADH dependent azoreductase of 32 kDa in size. Surprisingly, purified azoreductase showed the highest activity at 80 °C and pH 8.0. An increase in the activity of superoxide dismutase after decolorization confirmed the signature of oxidative stress and its involvement in the dismutation of reactive metabolites. Intermediate metabolite analysis by HPLC, GC-MS and FTIR and the removal of total organic carbon (TOC) suggested the azoaromatics’ degradation leads to mineralization via a TCA cycle.
N cleavage), subsequently underwent hydroxylation by the cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (CYP450) system. Azoreductase was purified by chromatographic techniques and characterization by MALDI-TOF substantiated its identity as FMN containing NADH dependent azoreductase of 32 kDa in size. Surprisingly, purified azoreductase showed the highest activity at 80 °C and pH 8.0. An increase in the activity of superoxide dismutase after decolorization confirmed the signature of oxidative stress and its involvement in the dismutation of reactive metabolites. Intermediate metabolite analysis by HPLC, GC-MS and FTIR and the removal of total organic carbon (TOC) suggested the azoaromatics’ degradation leads to mineralization via a TCA cycle.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...