Salts of 1-(chloromethyl)-1,1-dimethylhydrazine and ionic liquids†
Abstract
The reaction of 1,1-dimethylhydrazine with excess dichloromethane led to the formation of the chloride salt of the 1-(chloromethyl)-1,1-dimethylhydrazinium cation ([(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2]Cl, 1). The reaction of 1 with a suitable silver salt provided the nitrate ([(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2][NO3], 2), perchlorate ([(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2][ClO4], 3), azide ([(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2][N3], 4), dicyanamide ([(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2][N(CN)2], 5) and sulphate ([(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2]2[SO4], 6) salts. Compound 6 reacted with barium 5,5′-azobistetrazolate pentahydrate (Ba[N4C–N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–CN4]·5H2O), barium dipicrate tetrahydrate (Ba[(NO2)3Ph–O]2·4H2O) and barium 5-amino-1H-tetrazolate tetrahydrate (Ba[H2N–CN4]2·4H2O) to form the corresponding metathesis products: [(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2]2[N4C–N
N–CN4]·5H2O), barium dipicrate tetrahydrate (Ba[(NO2)3Ph–O]2·4H2O) and barium 5-amino-1H-tetrazolate tetrahydrate (Ba[H2N–CN4]2·4H2O) to form the corresponding metathesis products: [(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2]2[N4C–N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–CN4] (7), [(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2][(NO2)3Ph–O] (8) and [(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2][H2N–CN4] (9). Compounds 1–9 were characterized by elemental analysis, mass spectrometry, NMR (1H and 13C) and vibrational spectroscopy (infrared and Raman). Additionally, we measured the 15N NMR spectrum of the nitrate salt 2 and identified the solid state structure of compounds 3, 6, 7 and 8 by low temperature X-ray crystallography (3: Triclinic P
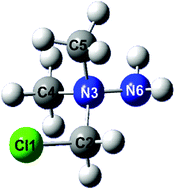
N–CN4] (7), [(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2][(NO2)3Ph–O] (8) and [(CH3)2N(CH2Cl)NH2][H2N–CN4] (9). Compounds 1–9 were characterized by elemental analysis, mass spectrometry, NMR (1H and 13C) and vibrational spectroscopy (infrared and Raman). Additionally, we measured the 15N NMR spectrum of the nitrate salt 2 and identified the solid state structure of compounds 3, 6, 7 and 8 by low temperature X-ray crystallography (3: Triclinic P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) , a = 5.983(1) Å, b = 7.502(1) Å, c = 9.335(1) Å; α = 93.86(1)°, β = 101.21(1)°; γ = 91.13(1)°; V = 409.8(1) Å3, 6: Monoclinic C2/c, a = 11.674(2) Å, b = 17.503(3) Å, c = 6.616(1) Å; β = 90.27(1)°; V = 1351.8(4) Å3, 7: Triclinic P
, a = 5.983(1) Å, b = 7.502(1) Å, c = 9.335(1) Å; α = 93.86(1)°, β = 101.21(1)°; γ = 91.13(1)°; V = 409.8(1) Å3, 6: Monoclinic C2/c, a = 11.674(2) Å, b = 17.503(3) Å, c = 6.616(1) Å; β = 90.27(1)°; V = 1351.8(4) Å3, 7: Triclinic P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) , a = 8.851(1) Å, b = 8.872(1) Å, c = 11.529(1) Å; α = 80.98(1)°, β = 83.47(1)°; γ = 71.37(1)°; V = 845.4(1) Å3 and 8: Monoclinic C2/c, a = 24.168(3) Å, b = 7.375(1) Å, c = 17.062(3) Å; β = 116.19(2)°; V = 1351.8(3) Å3). The solid state structure of barium dipicrate hexahydrate (Ba[(NO2)3Ph–O]2·6H2O) was also elucidated: Triclinic P
, a = 8.851(1) Å, b = 8.872(1) Å, c = 11.529(1) Å; α = 80.98(1)°, β = 83.47(1)°; γ = 71.37(1)°; V = 845.4(1) Å3 and 8: Monoclinic C2/c, a = 24.168(3) Å, b = 7.375(1) Å, c = 17.062(3) Å; β = 116.19(2)°; V = 1351.8(3) Å3). The solid state structure of barium dipicrate hexahydrate (Ba[(NO2)3Ph–O]2·6H2O) was also elucidated: Triclinic P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) , a = 6.641(1) Å, b = 11.588(1) Å, c = 15.033(1) Å; α = 84.64(1)°, β = 80.07(1)°; γ = 86.80(1)°; V = 1133.8(1) Å3. Furthermore, we studied the thermal properties of compounds 1–9 by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Salts 2–4, 8 and 9 fall within the category of ionic liquids. Lastly, the energetic salts were subjected to standard sensitivity tests and a software code was used to predict the detonation parameters and specific impulses of the compounds and their mixtures with an oxidizer.
, a = 6.641(1) Å, b = 11.588(1) Å, c = 15.033(1) Å; α = 84.64(1)°, β = 80.07(1)°; γ = 86.80(1)°; V = 1133.8(1) Å3. Furthermore, we studied the thermal properties of compounds 1–9 by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Salts 2–4, 8 and 9 fall within the category of ionic liquids. Lastly, the energetic salts were subjected to standard sensitivity tests and a software code was used to predict the detonation parameters and specific impulses of the compounds and their mixtures with an oxidizer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...