A divided potential driving self-discharge process for single-walled carbon nanotube based supercapacitors
Abstract
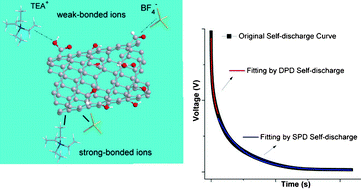
Understanding the self-discharge (SDC) mechanism is crucial for obtaining supercapacitors with tunable energy retention. Supercapacitors built with free standing

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...