Ultrafine Pt–Ru bimetallic nanoparticles anchored on reduced graphene oxide sheets as highly active electrocatalysts for methanol oxidation
Abstract
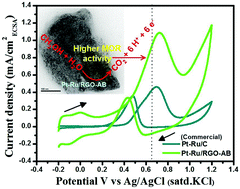
The controlled fabrication of bimetallic nanocatalysts with a suitable size, structure and morphology is extremely important to realize direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs) as promising energy-generating sources. In this paper, a facile approach for depositing platinum–ruthenium (Pt–Ru) bimetallic nanoparticles on a reduced graphene oxide (RGO) support has been demonstrated. Two electrocatalysts denoted as Pt–Ru/RGO-AA and Pt–Ru/RGO-AB were synthesized by synchronously reducing H2PtCl6 and RuCl3 on the graphene oxide (GO) support with reducing agents ascorbic acid and methyl ammonia borane, respectively. For comparison of methanol electrooxidation activity, monometallic Pt nanoparticles supported on RGO sheets (Pt/RGO) were also synthesized. All the catalysts were conveniently synthesized under ambient conditions without using any surfactants. The Pt/RGO, Pt–Ru/RGO-AA and Pt–Ru/RGO-AB electrocatalysts were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), selected area electron diffraction (SAED) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). Among all the catalysts, the Pt–Ru/RGO-AB catalyst with an average particle size of 2.8 nm possessed remarkable uniformity on the RGO sheets. The electrochemical performance of RGO-supported Pt and Pt–Ru catalysts towards methanol oxidation was systematically studied using cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry. The results demonstrate that the Pt–Ru/RGO-AB catalyst with a high electrochemical active surface area (ECSA) of 130.46 m2 g−1 exhibits a higher mass and ECSA normalized activities towards methanol oxidation. Furthermore, the Pt–Ru/RGO-AB catalyst has a better tolerance towards accumulated CO-like species as realized from its higher ratio of forward peak current density to reverse peak current density (If/Ib) of 3.21. The facile fabrication strategy described here is convenient and could be used for the fabrication of other multi-component nanostructured electrocatalysts for fuel cell reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...