Removal of Cr(iii)/Cr(vi) from wastewater using defective porous boron nitride: a DFT study†
Abstract
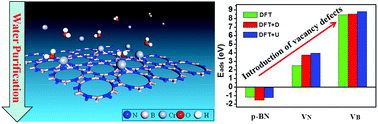
Developing highly-efficient adsorbent materials for the removal of Cr(III)/Cr(VI) ions from industrial wastewater is of great importance for environmental pollution control. In this work, density functional theory was used to model the adsorption capacities of Cr(III)/Cr(VI) ions on defective porous boron nitride (p-BN). Our results suggest that both nitrogen (VN) and boron (VB) vacancies contribute to the adsorption of Cr(III)/Cr(VI) ions on p-BN. In the case of a VN defect, the calculated adsorption energy (Eads) values are 3.76 eV and 4.58 eV for single Cr(III) and Cr(VI) ions, respectively, whereas, in the case of a VB defect, the Eads values are 8.55 eV and 10.26 eV for Cr(III) and Cr(VI) ions, respectively. The analysis of the electronic structure reveals that defective levels in the energy gap region strongly affect the adsorption performance of p-BN as an adsorbent. More importantly, we clarify that the strong adsorption of Cr(III)/Cr(VI) ions on defective p-BN is indeed chemical adsorption and not dispersion or electrostatic attraction. High coverage of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) ions and the effect of water solvent molecules were also taken into account. These findings indicate that defective p-BN is an excellent candidate for the removal of Cr(III)/Cr(VI) ions from wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...