In situ synthesis and photocatalytic mechanism of a cyano bridged Cu(i) polymer†
Abstract
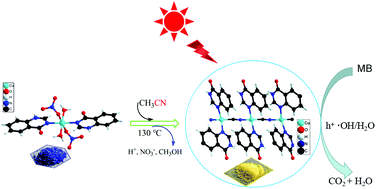
A one-dimensional copper(I) nanorod polymer [Cu(L)2·(CN)]n (1) (L = 4(3H)-quinazolone), was formed in situ by C–C bond cleavage of acetonitrile. The in situ synthesis of 1 was analyzed using electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) and its methylene blue (MB) photocatalytic degradation mechanism was revealed from density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The results are helpful for the in situ synthesis of –CN complexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...