New molecular insights into the stability of Ni–Pd hollow nanoparticles
Abstract
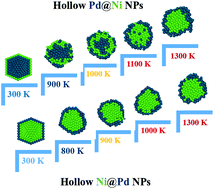
In this study, the thermal behaviors of pure Ni and Pd as well as Ni@Pd, and Pd@Ni hollow nanoclusters were investigated by MD simulations. The Ni@Pd hollow nanoclusters exhibited more thermodynamic stability and a higher melting point than the Pd@Ni ones. This result is opposite to the trend demonstrated by the corresponding bulk materials, which could be related to the effect of the hollow core. Due to the small difference between the melting points of bulk Pd and Ni, a two-step melting behavior was not observed for the hollow Pd–Ni nanoclusters. The differences between the thermodynamic stabilities of the simulated nanoclusters were related to the concentration of Pd atoms in the shell and Ni atoms in the core regions due to the lower surface energy of Pd atoms and the higher cohesive and binding energy of Ni atoms. Also, a larger nanocluster size led to a faster diffusion of Pd atoms toward the shell of the nanocluster. Moreover, the diffusion of Pd atoms to the surface and Ni atoms to the core region for Pd@Ni nanoclusters near the melting point and the increase in the ordered atoms under these circumstances led to a higher melting point of this nanocluster in comparison with the Ni@Pd nanoclusters. These results indicate the potential for the future construction of nanocatalysts based on bimetallic nanoclusters with core–shell hollow structures.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers HOT articles for 2017


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...