Cleavage of macromolecular RAFT chain transfer agents by sodium azide during characterization by aqueous GPC†
Abstract
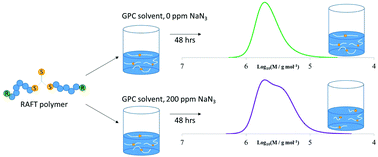
Accurate and reliable analysis of polymers by GPC is vital in the field of controlled radical polymerisation. Often, water-soluble polymers are analysed by aqueous gel permeation chromatography (GPC) in a solvent containing dilute sodium azide as an anti-microbial agent. Previous reports have shown that sodium azide at high concentration is able to remove terminal CTA groups from polymer chains, producing thiol-terminated polymers. This study demonstrates that GPC sample preparation of RAFT polymers in aqueous solvents containing dilute (200 ppm) sodium azide can cause significant changes in the measured molecular weight distribution. These changes occur within hours of dissolving the polymer sample and are shown to be due to cleavage of the CTA in the polymer chain together with disulfide coupling of the resulting polymeric thiols. The extent to which this occurs is strongly dependent on the CTA attached to the polymer; an almost 10-fold difference in the rate of CTA removal is observed between different RAFT agents. The by-product of the reaction between sodium azide and RAFT polymers is also investigated and shown to be an unstable thiatriazole-functionalised Z group. The thiatriazole then degrades further to form a nitrile-functionalised Z group, N2 and elemental sulfur.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...