Functionalizing natural polymers with alkoxysilane coupling agents: reacting 3-glycidoxypropyl trimethoxysilane with poly(γ-glutamic acid) and gelatin†
Abstract
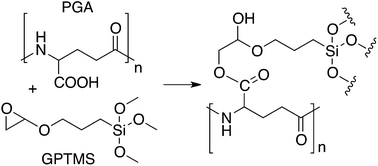
Hybrid materials, with co-networks of organic and inorganic components, are increasing in popularity due to their tailorable degradation rates and mechanical properties. To increase mechanical stability, particularly in water, covalent bonding must occur between the components. This can be introduced using crosslinking agents such as 3-glycidoxypropyl trimethoxysilane (GPTMS). Attachment of GPTMS to polymers in aqueous conditions is hypothesized to occur by opening of the epoxide ring by nucleophiles on the polymer chain. Despite side reactions that occur between the epoxide ring of GPTMS and water, a range of NMR techniques showed that the carboxylic acid group of poly(γ-glutamic acid) reacted with GPTMS. This result was used to identify the amino acids in gelatin that reacted most rapidly with the GPTMS epoxide ring, confirming that covalent bonding occurred in gelatin–silica hybrid materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...