Injectable cationic hydrogels with high antibacterial activity and low toxicity†
Abstract
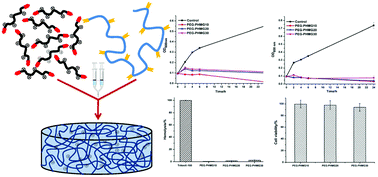
Antibacterial materials have always suffered from high toxicity. In this study, we fabricated injectable and biodegradable hydrogels utilizing poly(hexamethylene guanidine) hydrochloride and poly(ethylene glycol) as the backbone through a thiol–ene “click” reaction under physiological conditions, and they showed remarkably low toxicity and high and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...