Modulating the solubility of zwitterionic poly((3-methacrylamidopropyl)ammonioalkane sulfonate)s in water and aqueous salt solutions via the spacer group separating the cationic and the anionic moieties†
Abstract
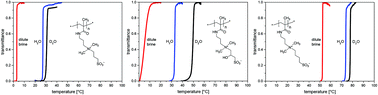
Complementary to the well-established zwitterionic monomer 3-((3-methacrylamidopropyl)dimethylammonio)propane-1-sulfonate (SPP), the closely related monomers 2-hydroxy-3-((3-methacrylamidopropyl)dimethylammonio)propane-1-sulfonate (SHPP) and 4-((3-methacrylamidopropyl)dimethylammonio)butane-1-sulfonate (SBP) were synthesised and polymerised by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerisation, using a fluorophore labeled RAFT agent. The polyzwitterions of systematically varied molar masses were characterised with respect to their solubility in water and aqueous salt solutions. Both poly(sulfobetaine)s show thermoresponsive behaviour in water, exhibiting phase separation at low temperatures and upper critical solution temperatures (UCST). For both polySHPP and polySBP, cloud points depend notably on the molar mass, and are much higher in D2O than in H2O. Also, the cloud points are effectively modulated by the addition of salts. The individual effects can be in parts correlated to the Hofmeister series for the anions studied. Still, they depend in a complex way on the concentration and the nature of the added electrolytes, on the one hand, and on the detailed nature of the spacer group separating the anionic and the cationic charges of the betaine moiety, on the other hand. As anticipated, the cloud points of polySBP are much higher than the ones of the analogous polySPP of identical molar mass. Surprisingly, the cloud points of polySHPP are also somewhat higher than the ones of their polySPP analogues, despite the additional hydrophilic hydroxyl group present in the spacer separating the ammonium and the sulfonate moieties. These findings point to a complicated interplay of the various hydrophilic components in polyzwitterions with respect to their overall hydrophilicity. Thus, the spacer group in the betaine moiety proves to be an effective additional molecular design parameter, apparently small variations of which strongly influence the phase behaviour of the polyzwitterions in specific aqueous environments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...