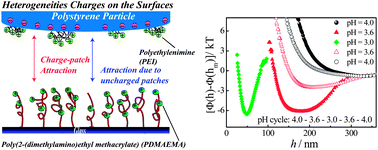
The manufacturing of switchable surfaces can be achieved when polymer chains are adsorbed or grafted densely on solid surfaces. These so-called “smart” surfaces have been often used to control the adsorption of various colloidal particles and biomolecules. To have an insight into the adsorption process, knowledge of the interaction forces between the surface and colloidal particle or biomolecule is critical. In this work, we used Total Internal Reflection Microscopy (TIRM) to directly measure the interaction potentials between poly(2-(dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate)) (PDMAEMA) brushes with two different lengths grafted on a glass slide and a positively charged polystyrene (PS) particle with pre-adsorbed layers of poly(ethyleneimine) (PEI, Mw = 2000 g mol−1), in aqueous solutions. As can be shown by direct interaction measurements, the interactions were strongly affected by the conformation of the polyelectrolyte brushes, pH values and salt concentrations. For short polymer brushes (∼30 nm), at pH 4.2 and 3.5 the interaction between the partially protonated and swollen PDMAEMA brush and the positively charged PS particle was dominated by repulsive forces at low salt concentrations, originating from diffuse layer overlap. However, when the pH is decreased to 3.0, a long-range attraction sets in. For longer polymer brushes (∼75 nm), the influences of the pH and salinity were more complex. Our results showed that the interaction between the longer polymer brushes and the particle could be switched reversibly between pure repulsion at pH 4.0, medium attraction at pH 3.6 and strong attraction at pH 3.0. The interaction mechanisms that act at these pH values and salt concentrations were discussed.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...