Controlled peptide coated nanostructures via the self-assembly of functional peptide building blocks
Abstract
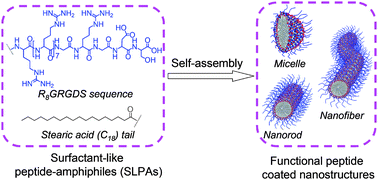
To realize the self-assembly of an arginine-rich peptide sequence of R8GRGDS with tumor-targeting and membrane-penetrating functions, a hydrophobic aliphatic tail (stearic acid, C18) was coupled to its N-terminus to construct surfactant-like peptide-amphiphiles (SLPAs). Through increasing the number of C18 tails to enhance the hydrophobic interactions, SLPA2 with two C18 tails and SLPA3 with four C18 tails can self-assemble into different nanostructures, including spherical micelles, nanorods and nanofibers in aqueous solution. Because the self-assembly of SLPA2 and SLPA3 is mainly driven by the hydrophobic interactions among the C18 tails, the random-coil conformation of the functional R8GRGDS sequence does not change during self-assembly and the resulting self-assembled nanostructures can be seen as a functional R8GRGDS sequence coated architecture. When using the self-assembled micelles of SLPA3 to load the anti-tumor drug of doxorubicin (DOX) and incubating with HeLa or COS-7 cells, the DOX loaded micelles can efficiently use the tumor-targeting and membrane-penetrating functions of their surface coated R8GRGDS sequences to deliver the drug into HeLa cells. The strategy reported here presents potential for the construction of biocompatible peptide-based biomaterials with favorable bioactivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...