Cationic amphiphilic Zn-porphyrin with high antifungal photodynamic potency
Abstract
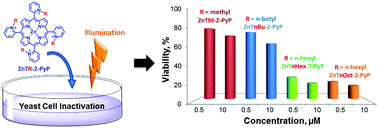
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a promising alternative approach particularly attractive for treatment of localized fungal infections. It is based on compounds, photosensitizers (PSs), which when excited with visible light, generate reactive species that ultimately cause cell death. Such species have short lifespans; as a consequence, efficiency and selectivity of the PDT treatment depend mainly on the properties of the PSs. This study is the first to explore the effect of cationic porphyrin-based photosensitizers on Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a member of the fungus kingdom. The study investigates which properties of the PS are essential for efficient antifungal PDT. Cationic Zn(II) meso-tetrakis(N-alkylpyridinium-2-yl)porphyrins (ZnP) with identical tetrapyrrole core and photo-physical properties, but with different substituents at the meso positions of the porphyrin ring were studied. Attaching six-carbon aliphatic chains to the four pyridyl nitrogens at all meso positions to the porphyrin ring produced a highly photo-efficient amphiphilic, water soluble PS, with minimal dark toxicity. It was taken up by the yeast cells and upon illumination suppressed metabolism by inactivating cytoplasmic and mitochondrial enzymes, and compromising plasma membrane barrier function. At low concentrations (up to 5 μM) the tetrahexyl derivative was a much more powerful antifungal agent than the commercially available chlorin e6. The more lipophilic tetraoctyl analog was also highly photo-efficient but displayed strong dark toxicity, presumably due to higher lipophilicity which might affect the lipid bilayer of membranes. Results presented here can assist the design of antifungal agents whose biological action depends on efficient and rapid uptake by the cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...