Sonochemical/hydration–dehydration synthesis of Pt–TiO2 NPs/decorated carbon nanotubes with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production activity
Abstract
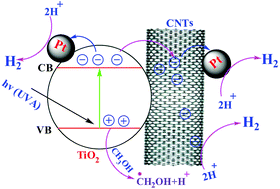
Modified Pt–TiO2 NPs/decorated carbon nanotubes were synthesized utilizing sonochemical/hydration–dehydration techniques. Pt was loaded on TiO2 by a photodeposition method keeping in mind the end goal to achieve electron–hole pair separation and promote the surface reaction. The morphological and basic properties of Pt–TiO2/fCNTs were investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), photoluminescence (PL) and Raman spectroscopy. The selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns of Pt–TiO2/fCNTs were obtained utilizing TEM-based energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDXS) analysis. It was found that the TiO2 nanoparticles were uniformly distributed on the fCNTs, and the Pt particles were decorated on the surface of TiO2/fCNTs. The photocatalytic hydrogen production activity of the Pt(0.5%)–TiO2/fCNTs(0.5%) nanoparticle composites was investigated using a sacrificial agent methanol solution. Pt-loaded TiO2 demonstrated a hydrogen evolution rate around 20 times that of TiO2/fCNTs(0.5%) (fSWCNTs, fMWCNTs). When compared with platinized TiO2 in methanol, which was utilized as a control material, Pt–TiO2/fCNTs demonstrated an almost 2-fold increment in hydrogen generation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...