Quantitative assessment of photostability and photostabilisation of Fluvoxamine and its design for actinometry
Abstract
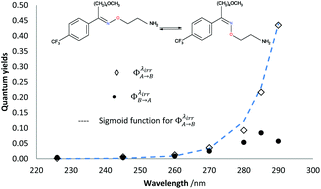
Despite the numerous concerns that have been raised in relation to considering 0th, 1st and 2nd-order kinetic treatments for photodegradation characterisation and assessment of drugs, they still are employed, as they are the only tools available for these types of studies. The recently developed Φ-order kinetic models have opened new perspectives in the treatment of photoreaction kinetics and stand as the best known alternative to the classical approach. The Φ-order kinetics have been applied here to Fluvoxamine (Fluvo) with the aim of setting out a detailed and comprehensive procedure capable of rationalising photodegradation/photostability of drugs and proposing a platform for photosafety studies. Our results prove that quantum yields of drugs (0.0016 < 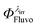 < 0.43) should a priori be considered wavelength-dependent; their photostabilisation (up to 75% for Fluvo) by means of absorption competitors can explicitly be related to a decrease of the photokinetic factor, and photoreversible drugs can be developed into efficient actinometers (as Fluvoxamine in the 260–290 nm range). A pseudo-rate-constant factor was proposed as a descriptive parameter, circumventing the limitations of overall rate-constants and allowing a comparison between kinetic data of drugs obtained under different conditions.
< 0.43) should a priori be considered wavelength-dependent; their photostabilisation (up to 75% for Fluvo) by means of absorption competitors can explicitly be related to a decrease of the photokinetic factor, and photoreversible drugs can be developed into efficient actinometers (as Fluvoxamine in the 260–290 nm range). A pseudo-rate-constant factor was proposed as a descriptive parameter, circumventing the limitations of overall rate-constants and allowing a comparison between kinetic data of drugs obtained under different conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...