Effects of a low-level semiconductor gallium arsenide laser on local pathological alterations induced by Bothrops moojeni snake venom
Abstract
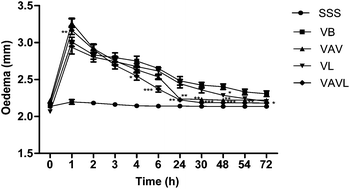
Antivenom therapy has been ineffective in neutralizing the tissue damage caused by snakebites. Among therapeutic strategies to minimize effects after envenoming, it was hypothesized that a low level laser would reduce complications and reduce the severity of local snake venom effects. In the current study, the effect of a low-level semiconductor gallium arsenide (GaAs) laser on the local pathological alterations induced by B. moojeni snake venom was investigated. The experimental groups consisted of five male mice, each administered either B. moojeni venom (VB), B. moojeni venom + antivenom (VAV), B. moojeni venom + laser (VL), B. moojeni venom + antivenom + laser (VAVL), or sterile saline solution (SSS) alone. Paw oedema was induced by intradermal administration of 0.05 mg kg−1 of B. moojeni venom and was expressed in mm of directly induced oedema. Mice received by subcutaneous route 0.20 mg kg−1 of venom for evaluating nociceptive activity and the time (in seconds) spent in licking and biting the injected paw was taken as an

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...