Competitive photocyclization/rearrangement of 4-aryl-1,1-dicyanobutenes controlled by intramolecular charge-transfer interaction. Effect of medium polarity, temperature, pressure, excitation wavelength, and confinement†
Abstract
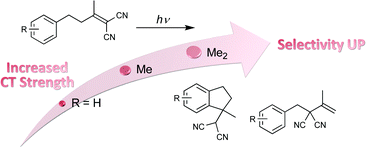
A series of 4-aryl-1,1-dicyanobutenes (1a–1f) with different substituents were synthesized to control the intramolecular donor–acceptor or charge-transfer (C–T) interactions in the ground state. Photoexcitation of these C–T substrates led to competitive
- This article is part of the themed collection: In honour of the contribution of Japanese scientists to photochemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...