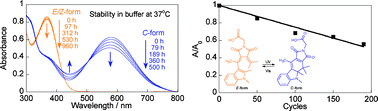
Photochromic fulgides and fulgimides have been identified as promising materials for applications in optical memory media, optical switches, and sensors. For applications in humid environments or biological systems, hydrolytic stability is crucial. A new photochromic methyl carboxylic acid indolylfulgimide was synthesized to improve hydrolytic stability in aqueous solution. The UV-vis spectra, extinction coefficient, thermal stability, and photochemical stability of the fulgimide were characterized in 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4). The open and closed forms were both stable in buffer. At 37 °C after 500 h, the open forms of the fulgimide showed no degradation within experimental error (1–2%) by 1H NMR and 2.3% decomposition by UV-vis spectroscopy. The closed form degraded 22% and 11% after 500 h at 37 °C in buffer by UV-vis and 1H NMR data, respectively. In addition, the fulgimide cycled back and forth between the open and closed forms 80 times before degrading by 20% in buffer. The methyl group at the bridging position of the fulgimide significantly increased the thermal stability by overcoming the rapid hydrolysis of the trifluoromethyl group.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...