Comparative efficiencies of the decolourisation of Methylene Blue using Fenton’s and photo-Fenton's reactions†
Abstract
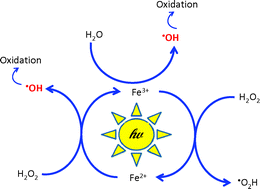
The decolourisation and
- This article is part of the themed collection: Solar chemistry and photocatalysis - environmental applications

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...