Rufloxacin induced photosensitization in bio-models of increasing complexity
Abstract
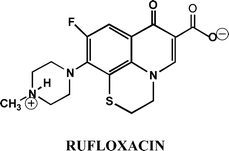
Rufloxacin belongs to the class of fluoroquinolones that act mainly as specific inhibitors of bacterial Topoisomerase II. These drugs are widely known to be involved in various diseases ranging from cutaneous reactions to aging. The type II photosensitizing activity of Rufloxacin has been already demonstrated on calf thymus DNA and free nucleosides. The aim of this study is to examine in control untreated and UVA irradiated human fibroblasts the modifications on DNA status induced by Rufloxacin added in the culture medium. This allows to investigate the photosensitizing activity of Rufloxacin in a more complex cell model. Fibroblasts, either in the presence or in the absence of Rufloxacin, were exposed to UVA irradiation for different times. An experimental protocol was followed in order to evaluate the amount of single-strand breaks (SSB) and double-strand breaks (DSB) DNA fragmentation by comet assay, and plasmid photocleavage. The presence of oxidized bases was also evaluated using the 8-OH-dGuo test. The comet assay test was also employed to assess cellular repair capacity. The intracellular drug concentration was verified by HPLC-MS. The results confirming the role of Rufloxacin as photosensitizer were: (i) a time-dependent increase in DNA fragmentation when fibroblasts were irradiated in the presence of Rufloxacin; (ii) the efficiency of the cellular repair machinery to be exhaustive after 2 h (whereas no correlation between irradiation time and DNA damage repair was observed with a higher level of DNA fragmentation after shorter irradiation times); (iii) the increased number of cells exhibiting high DNA fragmentation, seen as comets with long tails, was not accompanied by a similar large extent of oxidised DNA base formation, as measured by 8-OH-dGuo analysis; (iv) the double helix SSB, formed in plasmid photosensitization, agreed with the comet assay results, pointing out a good correlation among the cell system and the simpler models used.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...