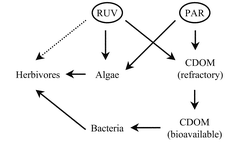
The role of ultraviolet radiation on shallow, high CDOM (colored dissolved organic matter) lakes was investigated during two consecutive summers (1999 and 2000) in replicated mesocosms (rectangular fiberglass tanks). Each tank (volume: 300 L; depth: 40 cm) was covered with a layer (∼3 cm) of sediment from lake El Toro (40° 14′ S; 70° 22′ W) and filled with filtered water. The experimental design consisted of two treatments: full natural radiation (UV-exposed) and natural radiation without ultraviolet radiation (UV-shielded). UV-exposed and UV-shielded treatments differed in most studied variables as revealed by repeated measures ANOVA. UV-exposed tanks displayed lower CDOM levels (dissolved absorbance) of lower average molecular size (absorbance ratio between 250 and 365 nm), higher bacterial biomass, and lower chlorophyll a concentration. The effect on consumers (rotifers and crustaceans) was less noticeable. The results are consistent with UV stimulation of bacteria production mediated by higher rates of CDOM photobleaching, and the photoinhibition of planktonic algae. Thus, a major effect of UVR in shallow, high CDOM ecosystems appears to be the stimulation of heterotrophic pathways and a simultaneous inhibition of photoautotrophs.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...