Comparison of the acid–base properties of purine derivatives in aqueous solution. Determination of intrinsic proton affinities of various basic sites†
Abstract
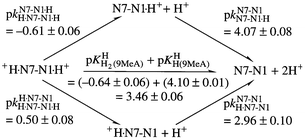
The acidity constants of protonated 7,9-dimethylguanine, 7-methylguanosine, 7,9-dimethylhypoxanthine, 7-methylinosine, 9-methyladenine, 1,9-dimethyladenine, 7,9-dimethyladenine and 1-methyladenosine were determined in aqueous solution at 25 °C and I = 0.1 M (NaNO3). In those instances where pKa > 2 potentiometric pH titrations were used for the determinations; when pKa < 2, UV spectrophotometric and 1H-NMR shift measurements were employed (25 °C). In these latter instances, where I is often larger than 0.1 M, the H0 scale was applied to define the H+ activity of the strong acid (HClO4; HNO3). A combination of the present results with values taken from our earlier work allowed us to quantify the intrinsic acidic properties in aqueous solution of the (N1)H0 or + and (N7)H+ sites via micro acidity constant schemes for seven purine derivatives and to calculate the tautomeric ratios regarding the monoprotonated species, that is N7–N1·H versus H·N7–N1 meaning that in one isomer H+ is at the N1 site and in the other at N7. A plot of the micro acidity constants pkN7–N1H·N7–N1, which quantify the acidity of the (N7)H+ site, versus the macro acidity constants pKa/(N1)H, which largely refer to the release of the proton from the (N1)H unit, results in a straight line for the guanine and hypoxanthine derivatives. This fact allows estimation of the micro acidity constant for any related derivative provided a value for pKa/(N1)H is known. The presented results are also meaningful for nucleic acids because they quantify the acid–base properties of their individual sites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...