Atroposelectivity in the electrophilic substitution reactions of laterally lithiated and silylated tertiary amides
Abstract
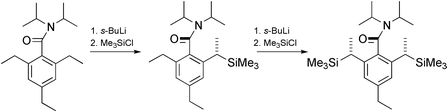
Lateral lithiation–electrophilic quench of 2-alkyl-1-naphthamides and 2,6-dialkylbenzamides yields products containing an atropisomeric Ar–CO axis and a new stereogenic centre with high (generally >95 ∶ 5) diastereoselectivity. With imines as electrophiles, single diastereoisomers containing an atropisomeric axis and two new stereogenic centres are formed. 2,6-Dialkylbenzamides may be functionalised stereoselectively at both the 2- and 6-positions, leading (with imines) to symmetrical compounds bearing 1,7-related stereogenic centres. 2-Alkylbenzamides with only one ortho alkyl group are not atropisomeric at ambient temperature but are functionalised diastereoselectively by lateral lithiation–electrophilic quench at −78 °C. Stabilisation of the atropisomeric products by further lithiation and alkylation proves their diastereoselective formation. The lack of stereospecificity in the fluoride-promoted reaction of a laterally silylated 1-naphthamide with an aldehyde suggests that reported reactions of laterally silylated benzamides may also be controlled by the rotationally restricted amide group.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...