Arginine modification of lycosin-I to improve inhibitory activity against cancer cells
Abstract
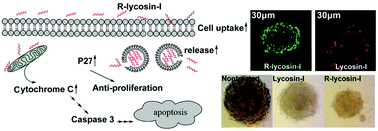
Lycosin-I is a linear amphipathic α-helical anticancer peptide (ACP) extracted from the spider Lycosa singoriensis, which can activate the mitochondrial death pathway to induce apoptosis in tumor cells and up-regulate p27 to inhibit cell proliferation. However, the applicability of lycosin-I as a novel anticancer drug is limited by its low cellular entry and efficacy in solid tumors. Amino acid substitution presents an effective and modest strategy to improve the anticancer activity and bioavailability of ACPs. Herein, an arginine-modified lycosin-I (named R-lycosin-I) was designed and synthesized by substituting lysine (Lys) with arginine (Arg). This peptide exhibited higher anticancer activity and penetrability against solid tumor cells than lycosin-I. They displayed noticeable differences in their physicochemical properties including the secondary structure, hydrodynamic size, and zeta potential. Fluorescence analyses have confirmed that R-lycosin-I exhibits increased cellular uptake and improved intracellular distribution. Due to its superior physical and chemical properties and high serum stability, R-lycosin-I could penetrate deeply into tumor spheroids and produce strong toxicity in the 3D tumor model. Overall, these findings suggest that arginine modification may provide an effective strategy for improving the anticancer activity of lycosin-I, and R-lycosin-I may be a useful lead for developing anticancer drugs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...