α-Tocopherol derived lipid dimers as efficient gene transfection agents. Mechanistic insights into lipoplex internalization and therapeutic induction of apoptotic activity†
Abstract
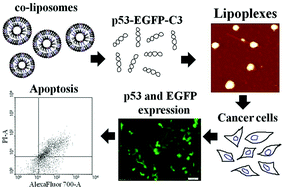
In this report, we present cationic dimeric (gemini) lipids for significant plasmid DNA (pDNA) delivery to different cell lines without any marked toxicity in the presence of serum. Six gemini lipids based on α-tocopherol were synthesized, which differed in their spacer chain lengths. Each of these gemini lipids mixed with a helper lipid, 1,2-dioleoyl phosphatidyl ethanolamine (DOPE), was capable of forming stable aqueous suspensions. These co-liposomal systems were examined for their potential to transfect pEGFP-C3 plasmid DNA into nine cell lines of different origins. The transfection efficacies noticed in terms of EGFP expression levels using flow cytometry were well corroborated using independent fluorescence microscopy studies. Significant EGFP expression levels were reported using the gemini co-liposomes, which counted significantly better than one well known commercial formulation, Lipofectamine 2000 (L2 K). Transfection efficacies were also analyzed in terms of the degree of intracellular delivery of labeled plasmid DNA (pDNA) using confocal microscopy, which revealed an efficient internalization in the presence of serum. The cell viability assays performed using optimized formulations demonstrated no significant toxicity towards any of the cell lines used in the study. We also had a look at the lipoplex internalization pathway to profile the uptake characteristics. A caveolae/lipid raft route was attributed to their excellent gene transfection capabilities. The study was further advanced by using a therapeutic p53-EGFP-C3 plasmid and the apoptotic activity was observed using FACS and growth inhibition assay.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recognition and Reactivity at Interfaces

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...