Enthalpy-driven nuclease-like activity and mechanism of peptide–chlorambucil conjugates†
Abstract
We report the results of attaching the anticancer drug chlorambucil (CLB) to two high-affinity DNA binding peptides: Met-Hyp-Arg-Lys-(Py)4-Lys-Arg-NH2 (HyM-10) and Gln-Hyp-Arg-Lys-(Py)4-Lys-Arg-NH2 (HyQ-10). These CLB–peptide conjugates cleave DNA very effectively and sequence-selectively without the use of chemicals, heat, or UV irradiation. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis identifies the sites where CLB–HyM-10 and CLB–HyQ-10 attack a complementary pair of 5′-32P-labeled duplexes derived from pBR322 in the absence of piperidine or other chemical additives. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) has confirmed the preferential cleavage sites as well as a novel stepwise cleavage mechanism of sequence-selective DNA cleavage. Resembling restriction endonucleases, the CLB–peptide conjugates appear to be capable of producing double strand DNA breaks. Circular dichroism studies show that CLB–HyM-10 and CLB–HyQ-10 induce significant local conformational changes in DNA via the minor groove, possibly with dimeric binding stoichiometry. The energetic basis of DNA binding by these conjugates has been investigated by isothermal titration calorimetry, revealing that the binding of both the peptides and their CLB conjugates is overwhelmingly enthalpy-driven. The maintenance of a conserved negative binding free energy in DNA–conjugate interactions is a crucial feature of the universal enthalpy–entropy compensation phenomenon. The strongly enthalpy-driven binding of CLB–peptide conjugates to preferred loci in DNA furnishes the required proximity effect to generate the observed nuclease-like sequence-selective cleavage.
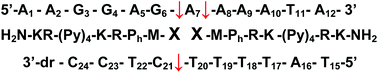

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...