Syntheses and biological evaluation of 2-amino-3-acyl-tetrahydrobenzothiophene derivatives; antibacterial agents with antivirulence activity†
Abstract
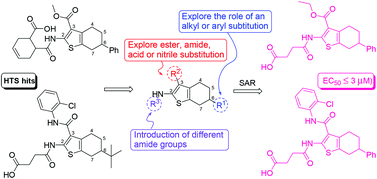
Developing new compounds targeting virulence factors (e.g., inhibition of pilus assembly by pilicides) is a promising approach to combating bacterial infection. A high-throughput screening campaign of a library of 17 500 small molecules identified 2-amino-3-acyl-tetrahydrobenzothiophene derivatives (hits 2 and 3) as novel inhibitors of pili-dependent biofilm formation in a uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain UTI89. Based on compounds 2 and 3 as the starting point, we designed and synthesized a series of structurally related analogs and investigated their activity against biofilm formation of E. coli UTI89. Systematic structural modification of the initial hits provided valuable information on their SARs for further optimization. In addition, small structural changes to the parent molecules resulted in low micromolar inhibitors (20–23) of E. coli biofilm development without an effect on bacterial growth. The hit compound 3 and its analog 20 were confirmed to prevent pili formation in a hemagglutination (HA) titer assay and electron microscopy (EM) measurements. These findings suggest that 2-amino-3-acyl-tetrahydrobenzothiophenes may serve as a new class of compounds for further elaboration as antibacterial agents with antivirulence activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...